- Carbohydrate is one of the four macro-molecules .
- The main function of carbohydrates is to store energy. They are the main energy source in living organisms.
- Carbohydrates contain carbon, oxygen and hydrates only.
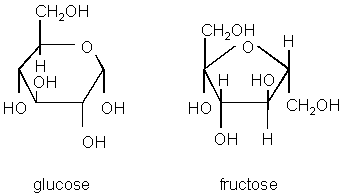
- Monosaccharide can be divided into Aldoses and ketoses. Aldoses are the sugars that contain an aldehyde group at the end such as glucose. Differently, ketoses have a ketone group (most likely at C2) , one of the examples of ketoses is Fructose.
- Sugars are usually seen in pentatoses ( 5 carbons ) or hexoses (6 carbons ). In order to become stable, they generally would form a ring at where the carbonyl group is at.
- Fructose and glucose are both hexoses, even though fructose forms a ring of five carbons with one extra carbon attaches on the C5.
- Sugars are not plain 2D diagrams but in real life it can be presented into two ways -- "chair" and "boat".However chair form is more stable.

- Glycosidic bonds are formed when two sugars combine though a process of condensation (dehydration synthesis) . In which the water is produced in order to link two carbohydrates together.
- Opposite to condensation is the synthesis of hydrolysis. The process of separate two sugars by adding in the water.
- Disaccharides means the molecule combined from two monosaccharides. Examples of disaccharides are : maltose, a starch formed by two glucose (C1-4). Sucrose, commonly known as table sugar in which is formed by glucose and fructose. Lactose, it is found in the milk and formed from galactose with glucose.
- The shape of α linkage looks like two molecules are "holding hands" and "pointing". Examples: Maltose, Sucrose.

- The shape of β linkage is looks more similar as a straight line rather than α linkage. Example: Lactose.

- Carbohydrate polymers ( such as starch, glycogen and cellulose ) are formed from many monosaccharides connected together with glycosidic linkages.
- Amylose is a glucose polymer with α(1-4) linkages. It normally presents in a single helix shape.
- Amylopection is a glucose polymer with mainly α(1-4) linkage, but few of α(1-6) linkages in which is able to produce multiple chains.
- The polymer of energy storage in animals is called glycogen, in which is a glucose polymer with α(1-4) linkages and α(1-6) linkages. However, it contains more α(1-6) linkages than amylopectin so it is able to form more branches than amylopectin.
- In order for the plant cells to keep its shape, the cell walls of plant cells contains cellulose. Cellulose has long chains of glucose with β(1-4) linkages in which stabilizes its shape.
- Humans are unable to digest cellulose in the plants ( such as grass or vegetables) due to the lack of the appreciate enzyme to breakdown the β linkages. Unlike humans, animals such as sheep or cow has the symbolic enzymes in the intestinal tract that allows them to digest the plants.
- Oligosaccharides means few monosaccharides are joined together either in linear or branched chains. They covalently attached to proteins or to membrane lipids.
- Selectins are integral proteins of the plasma membrane with lectin-like domain that protrude on the outer surface of mammalian cells.
Saturday, 24 March 2012
20 Facts on Carbohydrat
Friday, 2 March 2012
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)



